
Brief: a Loving Heart
Hanna is the first child ever to come from Myanmar (Burma) to undergo free congenital heart surgery at Wolfson Medical Center in Holon as part of the Save A Child Heart program.
All company news and stories

Hanna is the first child ever to come from Myanmar (Burma) to undergo free congenital heart surgery at Wolfson Medical Center in Holon as part of the Save A Child Heart program.

Have a happy and safe Independence Day weekend!
For older women with early-stage breast cancer, measures of health-related quality of life (HRQOL) predict 10-year mortality independently of traditional breast cancer prognostic variables, according to a study published online March 13 in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.

Patients with Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia commonly experience the sundown syndrome - a sudden worsening of confusion, agitation and aggression at the end of the day. Its daily pattern suggested that "sundowning," as the phenomenon is also known, may be governed by the body's internal biological clock. Synchronized by light and darkness, the circadian clock exerts control over wake/sleep cycles, body temperature, digestion, hormonal cycles and other physiological and behavior patterns. But whether the circadian clock regulated aggressive behavior was unknown.
A new blood test has been found to more accurately predict the development of tuberculosis up to two years before its onset in people living with someone with active TB, according to research published online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, an American Thoracic Society journal.
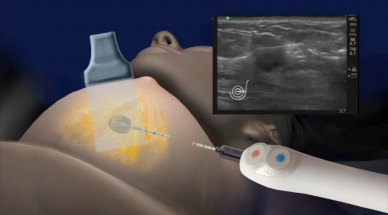
Treating cancer is often a notoriously long and trying process, sometimes requiring a combination of surgery and radiation or chemotherapy. These treatments can go on for months or longer, and come with a number of devastating side effects.

Most of the human genome—98 percent—is made up of DNA but doesn't actually encode genes, the recipes cells use to build proteins. The vast majority of genetic mutations associated with cancer occur in these non-coding regions of the genome, yet it's unclear how they might influence tumor development or growth. Now researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center have identified nearly 200 mutations in non-coding DNA that play a functional role in cancer. Each of the mutations could represent a new target in the search for cancer drugs.
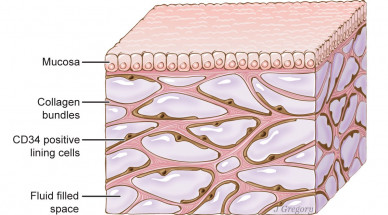
Researchers have identified a previously unknown feature of human anatomy with implications for the function of all organs, most tissues and the mechanisms of most major diseases.
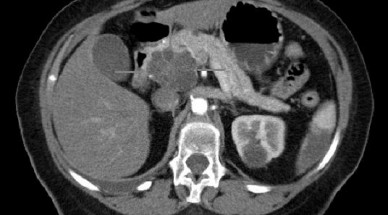
The population of bacteria in the pancreas increases more than a thousand fold in patients with pancreatic cancer, and becomes dominated by species that prevent the immune system from attacking tumor cells.